How to understand the logic ECU manufacturers use
If you are new to the field of engine reprogramming, you have surely quickly had to familiarize yourself with the specific terms of this industry. To assess the feasibility and complexity of modifying an engine, it is essential to refer to the engine control unit (ECU). However, there is a wide variety of ECUs, which can make navigation in this field quite complex. Fortunately, some equipment manufacturers, such as Bosch, have taken a logical approach to designating these ECUs, which can serve as a reference point. Here are some tips to help you navigate this diversity of ECUs:
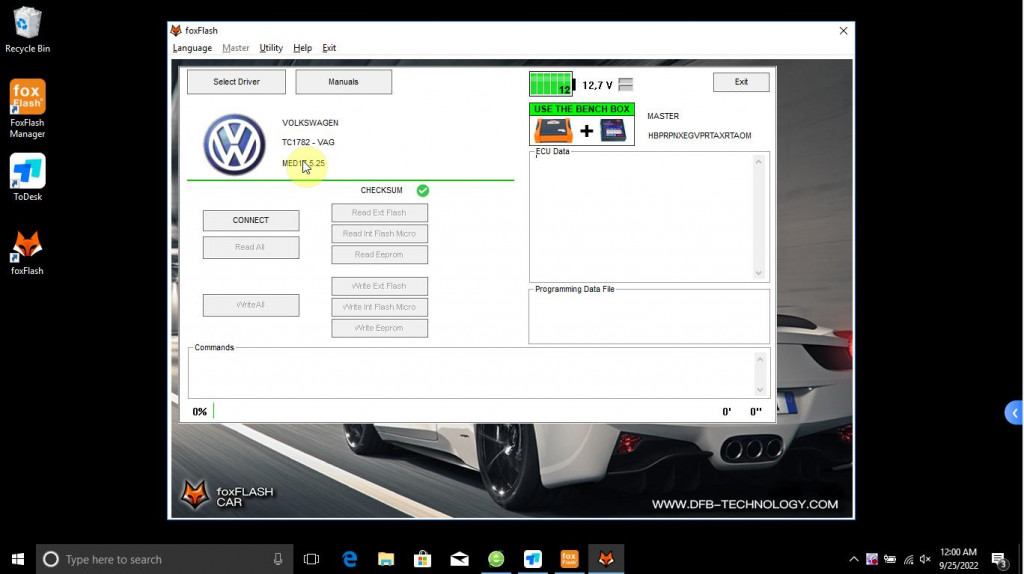
MED17.1.1
M: Motronic – This is the name given to the electronic control unit by Bosch.
E: Electronic throttle control system (not cable-operated).
D: Direct injection system.
17: Bosch version of the ECU.
1.1: ECU type (reserved for VAG here).
MG1CS201
M: Motronic – This is the name given to the electronic control unit by Bosch.
G: Gasoline – This is a gasoline engine.
1: Bosch version of the ECU.
C: Common rail – This is a common rail injection system.
S: Solenoid – These are solenoid injectors.
201: ECU type (reserved for BMW here).
MD1CP002
M: Motronic – This is the name given to the electronic control unit by Bosch.
D: Diesel – This is a diesel engine.
1: Bosch version of the ECU.
C: Common rail – This is a common rail injection system.
P: Piezo – These are piezo-electric injectors.
002: ECU type (reserved for Mercedes here).